Backend developer is a develop who maintain the work users / clients can't see such as processing transaction, data structure, data transfer. These works would contains in a API server and API server contains many endpoint that can call by anyone but only success when fulfill endpoint requirements so it is secured.
API Server
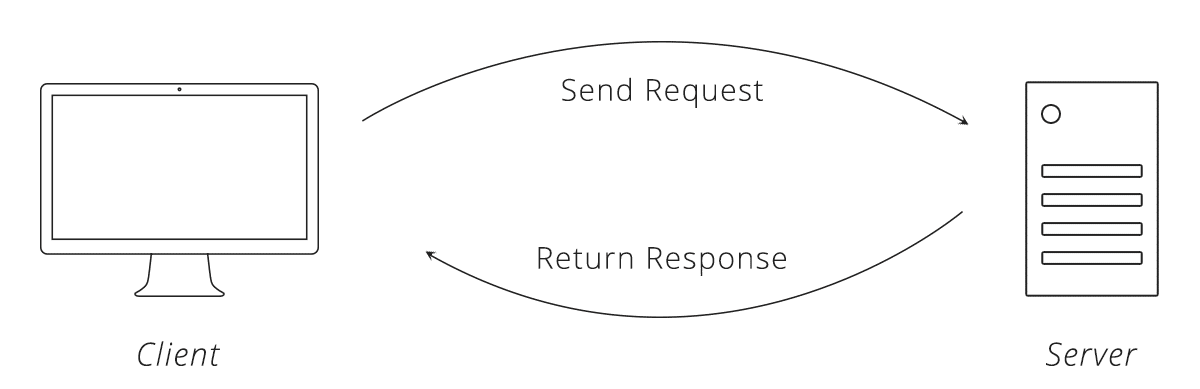
also know as REST API ( Representational State Transfer ). It's processing like client request to server & after server process return response to client.API Server is develop by backend developer and this api server can be many type and different language, different framework such as
- Ruby on Rails ( RoR ) using Ruby
- Python
- PHP ( Laravel & Yii2 )
- Java ( Spring )
- C# ( ASP.NET & NancyFX )
- Node.JS ( ExpressJS, SailsJS, HapiJS, NestJS, FeatherJS )
- MySQL
- PostgreSQL
- MongoDB
- Oracle
- Microsoft SQL Database
- Firebase ( realtime database )
- Firebase ( Realtime Database, Authentication, CDN )
- One Signal ( Notification )
- Here WeGo / Google Maps ( Maps )
- Docker ( Packaging apps )
- Docker Composer ( Container for storing docker app )
- Kubernetes [ k8s ] ( Container for storing docker app )
Backend Components
Most of the backend frameworks has almost same components / structures. They would have controller for processing data, router for map api to url and middleware for pre-access of incoming requests ( means that will run before controller ). If framework come with some data mapper, they would have models / entities for database objects, migration for scripting table of database objects, and lifecycle for handling lifecycle of models like ( beforeAction & afterAction ). Some of the framework or data mapper still have extra features for this but i not going to explain that cause still have some different on all of the framework but these 6 is most common at all backend frameworks. Before move on to these components i will explaining about requests & responses.Next part will talk about incoming requests & responses.